Geospatial Artificial Intelligence and Information Sharing (GAINS)
Area Skills
The thematic area "Geospatial Artificial Intelligence and Information Sharing" (GAINS) brings together the research activities of the Institute relating to the development and use of digital methodologies for the sharing and processing of geospatial resources (eg satellite and -situ) for Earth and Environmental Sciences applications. With respect to the strategic priorities identified by the European Commission for the period 2019-20241, the GAINS thematic area is in the direction of contributing to the development of the European Digital Strategy2 - with particular reference to the sectors relevant to the Institute identified in the European Green Deal3. Among the main components of the European Digital Strategy we should note the actions on the European Data Strategy and the Excellence and Trust in Artificial Intelligence.
At an international level, a relevant framework for the thematic area is the Group on Earth Observation (GEO), an inter-governmental organization to which over 100 Member States and over 100 POs (Participating Organizations) belong. . One of the main purposes of GEO is the development of GEOSS (Global Earth Observation System of Systems), a global infrastructure for sharing geospatial data provided by GEO members. In the GEO area, the regional components called Regional GEO have been activated; for Europe the regional reference component is EuroGEO5. EuroGEO enables Europe to position itself as a global force in Earth observation thanks to the extensive knowledge gained through the implementation of the Copernicus program and other initiatives. Finally, at the international level, the activities of the United Nations “Agenda 2030 for sustainable development” [2] program regarding the development of solutions for monitoring the Sustainable Development Goals6 (SDG) are of particular interest.
Area contact person: Mattia Santoro

The sharing of data and knowledge, especially at an interdisciplinary level, is today recognized as one of the keys to scientific progress and technological innovation.
The main activities carried out within the thematic area are:
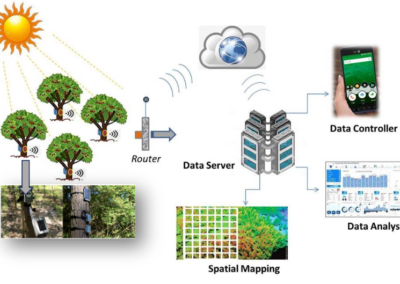
Design, development and operation of advanced infrastructures for sharing geospatial data: the Institute develops and maintains the GEO Discovery and Access Broker (GEO DAB). GEO DAB is one of the main components of the GEOSS Platform, the set of components that implement GEOSS; GEO DAB is a brokerage framework that allows interoperability with over 190 systems that contribute to GEOSS; o the Institute implements and maintains the WHOS-broker framework, which achieves interoperability between the different hydrological systems, making it possible to search and access hydrological data on a global scale, while at the same time guaranteeing a high quality of service. WHOS-broker is a component of the WHOS infrastructure built by the hydrological commission (CHy) of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
Design and development of solutions for the interoperability of environmental computational models and their execution on different cloud platforms: o The Virtual Earth Laboratory (VLab) framework, developed as part of H2020 projects, has the task of facilitating the publication of existing models for their execution in a multi-cloud environment. In the GEO / EuroGEO context, the VLab was tested within the GEOSS Platform and used to develop the demo shown by the European Commission at the GEO XVI Plenary as a contribution of the EuroGEO regional component to GEO.
Furthermore, VLab is used in the H2020 ERA-PLANET project for the implementation and execution of models useful for monitoring some of the indicators defined within the UN SDG.
- Experimentation of solutions based on the use of Artificial Intelligence techniques for the implementation of Digital Twin in the field of Earth and environmental sciences;
- Design and development of solutions for the formalization and sharing of knowledge (Knowledge Base);
LABORATORIES AND INSTRUMENTS
VLAB laboratory
The VLab framework responds to the needs of scientists and model makers, facilitating knowledge generation in evidence-based decision-making processes to address complex challenges at the local, regional and global levels.
Smart Technologies for Earth Observation
The Smart Technologies for Earth Observation (ST4EO) laboratory is a reality of the Institute on Atmospheric Pollution that operates nationally and internationally for the development of observational methodologies useful for the description of the phenomena occurring on ...
WHOS
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has created the WMO Hydrological Observing System (WHOS), which consists of a network of hydrological organizations on a global scale connected by a software platform (WHOS broker) capable of sharing data ...
GEOSS
A central part of the mission of the global intergovernmental organization GEO is to implement the Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS). GEOSS is a set of coordinated and independent Earth observation, information and processing systems ...