Earth observation: development of devices and methodologies for environmental analysis
Area Skills
Earth Observation (OT) consists of data collection, both from remoto that in situ, from multiple sources and in their processing in order to extract useful information to generate knowledge about the physical, chemical and biological processes of the Earth (variables, indices, indicators), with the aim of monitoring their state and changes, both of natural and anthropogenic origin. The application fields of OT techniques fall within the climate sciences, in the definition and evaluation of new policies for the sustainable management of natural resources, in the protection of ecosystems, in the mitigation of risks and the protection of human health, as well as in the promotion of eco-sustainable growth in economic and social field.
The scientific activities of the OT Group of the CNR-IIA fall within a wider community such as the Group on Earth Observations Committee on Earth Observation Satellite (GEO) which represents an intergovernmental partnership that aims to increase availability, access and the use of OT data and techniques to improve the health of the planet. GEO therefore promotes an open, free and coordinated sharing of OT data and infrastructures in order to improve research, as well as the decision-making and implementation processes of numerous disciplines. To this end, the GEO community is committed to developing the Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) for the benefit of all humanity. Copernicus, the Earth Observation Program of the European Union, fits into this context, which looks to our planet and its environment for the maximum benefit of all European citizens.
The activity of the researchers belonging to the thematic area Earth Observation: Development of Devices and Methodologies for the environmental analysis of the IIA, aims to integrate multi-source data through the use of artificial intelligence techniques and data systems cube and cloud computing on European platforms that provide access to Copernicus data (known as Data and Information Access Services, DIAS) and to extract all the information useful for generating new knowledge.
Area contact person: Maria Adamo

The richness and complementarity of skills, ranging from calibration, analysis and publication of data, to products and models (algorithms) in the GEO and EuroGEOSS field, constitutes a strength of the Institute in facing the challenges related to upcoming sustainable development goals.
The analysis of the essential variables, the main indicators and the temporal trends of change will have the dual objective of:
- give transversal support to the other thematic areas of the Institute, for example through the study of the spatial distribution of atmospheric pollutants, the main object of study by the IIA researchers;
- make data, models and knowledge available, through the use of GIS (Geographical Information Systems) and Virtual Laboratories developed by the thematic area relating to the sharing of geospatial information, to support the activities of the Copernicus program and environmental policies which see the main involvement of the GEO group, such as the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Paris Climate Agreements, and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.
In this context, it is useful to underline some aspects of the activity carried out by the researchers belonging to this thematic area. The first relates to the importance of the in-situ data acquisition activity, for the purposes of the calibration and validation of remote sensing data and derivative products (core and downstream services). Considerable interest is also addressed to the atmospheric component of the OT data and to the development of algorithms for the atmospheric correction of images. In this context, skills have been developed both in the study of the radiometric response of different surfaces, natural and non-natural, and in the study of radiative transfer into the atmosphere. Furthermore, the use of data from new generation satellites (eg, SENTINEL-5P) and ground data will be aimed at monitoring air quality in urban and rural contexts.
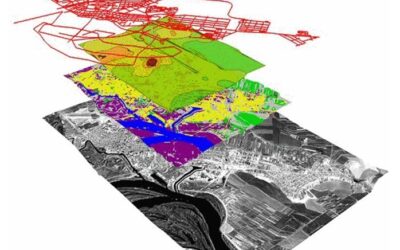
The spectral range of interest is that of VIS, NIR, SWIR and TIR, offered by both multi-spectral and hyper-spectral missions. In fact, the IIA has developed considerable experience in recent years in the analysis of both airborne (MIVIS) and field / laboratory hyper-spectral data, fundamental for the data analysis of the new PRISMA mission of the Italian Space Agency (ASI). for the integrated management of the territory. This knowledge has been used over the years for the development of innovative methods useful for the study of particular environmental problems such as the detection and evaluation of the wear of asbestos-cement roofs and the monitoring of areas subject to controlled and non-controlled landfills. Furthermore, the application of complex multi-source data flows allows the applicability of these techniques to heterogeneous contexts such as precision agriculture, the separation of plastic polymers, the retrieval of the above ground biomass and the wear of bituminous conglomerates.
Other relevant knowledge and experiences have been acquired in the analysis of data from active Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems, airborne or mounted on satellite platforms. The most recent and future SAR applications concern in particular:
a) high resolution extraction of wind fields, considered an essential variable for monitoring the climate and ecosystems in marine-coastal areas;
b) monitoring of infrastructures in urban ecosystems;
c) integration with optical data, for the classification of land cover in areas affected by cloud cover.
As part of projects funded by the European Community (HORIZON 2020) and by national and regional Bodies, the applications of OT data and techniques mainly concern the monitoring of biodiversity and natural and urban ecosystems, the monitoring of areas of archaeological interest, to particular environmental criticalities and the technological development inherent in precision agriculture. In this context, the IIA has actively collaborated with the Public Administrations, creating thematic maps to support decision-making systems.
Area capacity
The research area "Earth observation" has research and technical personnel with high qualifications in terms of competences, skills and responsibilities, they also collaborate in the projects and work of the Institute. workshops and missions.
LABORATORIES AND INSTRUMENTS
Radiometry laboratory
The Laboratory activities focus on the analysis of interaction phenomena between electromagnetic radiation (natural context or controlled lighting conditions) and objects. Through this type of investigation it is possible to define relationships...
Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) Laboratory
The study of the Earth through the use of drones allows to obtain very accurate data of the earth's surface. The use of optical sensors (e.g. RGB, multi/hyperspectral, thermal, LIDAR) or advanced (e.g. electrochemical type) allows in fact to obtain...
Smart Technologies for Earth Observation
The Smart Technologies for Earth Observation (ST4EO) laboratory is a reality of the Institute on Atmospheric Pollution that operates nationally and internationally for the development of observational methodologies useful for the description of the phenomena occurring on ...
Geomatics Laboratory
Geomatics (from the Greek Γη = Earth + μαθαίνω = learning + τέχνη = art; “the art of learning the Earth”) is an integrated and multidisciplinary approach, useful for studying the two-dimensional and three-dimensional distribution of the earth's surface as a function of ...